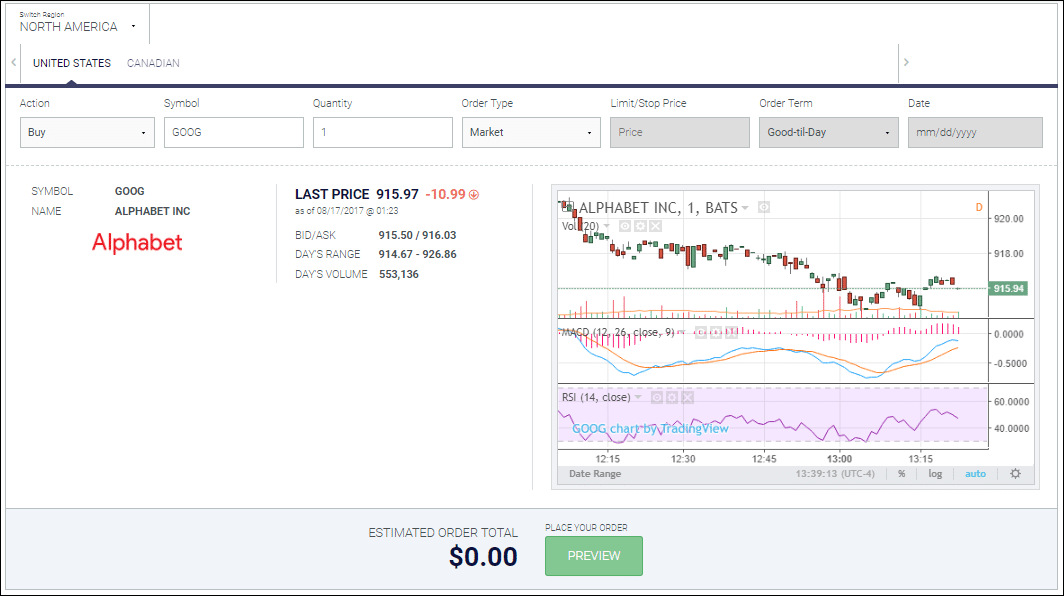
A long stock is an expression used when you own shares of a company. It represents a claim on the company’s assets and earnings. As you increase your holdings of a stock, your ownership stake in the company increases. Read this post to learn about the components of a long stock, and what it looks like graphically.
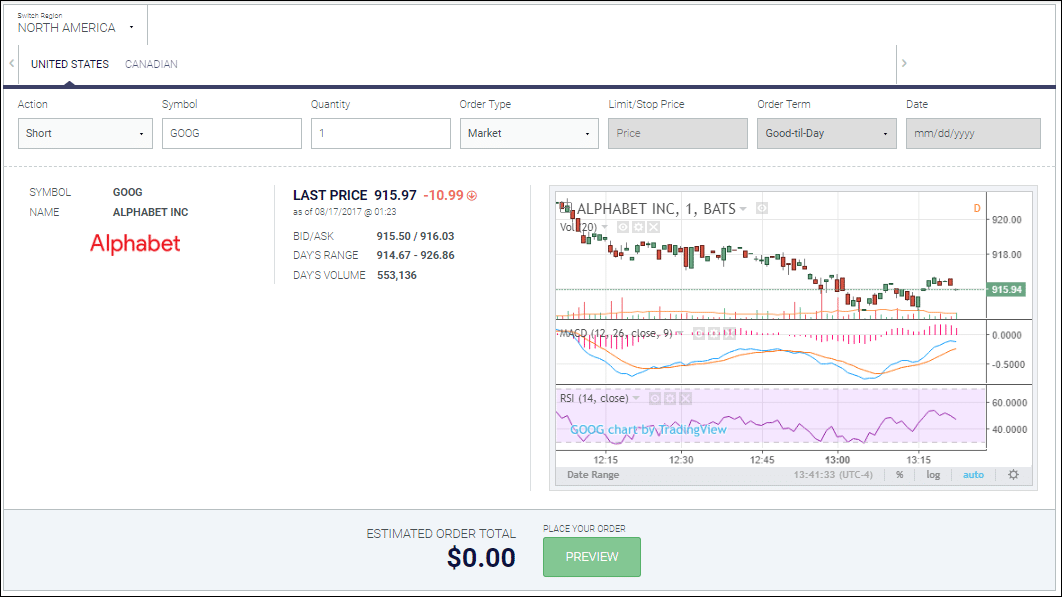
A short stock is an expression used when you sold shares of a company that you did not own beforehand, and is described in more detail in this post!
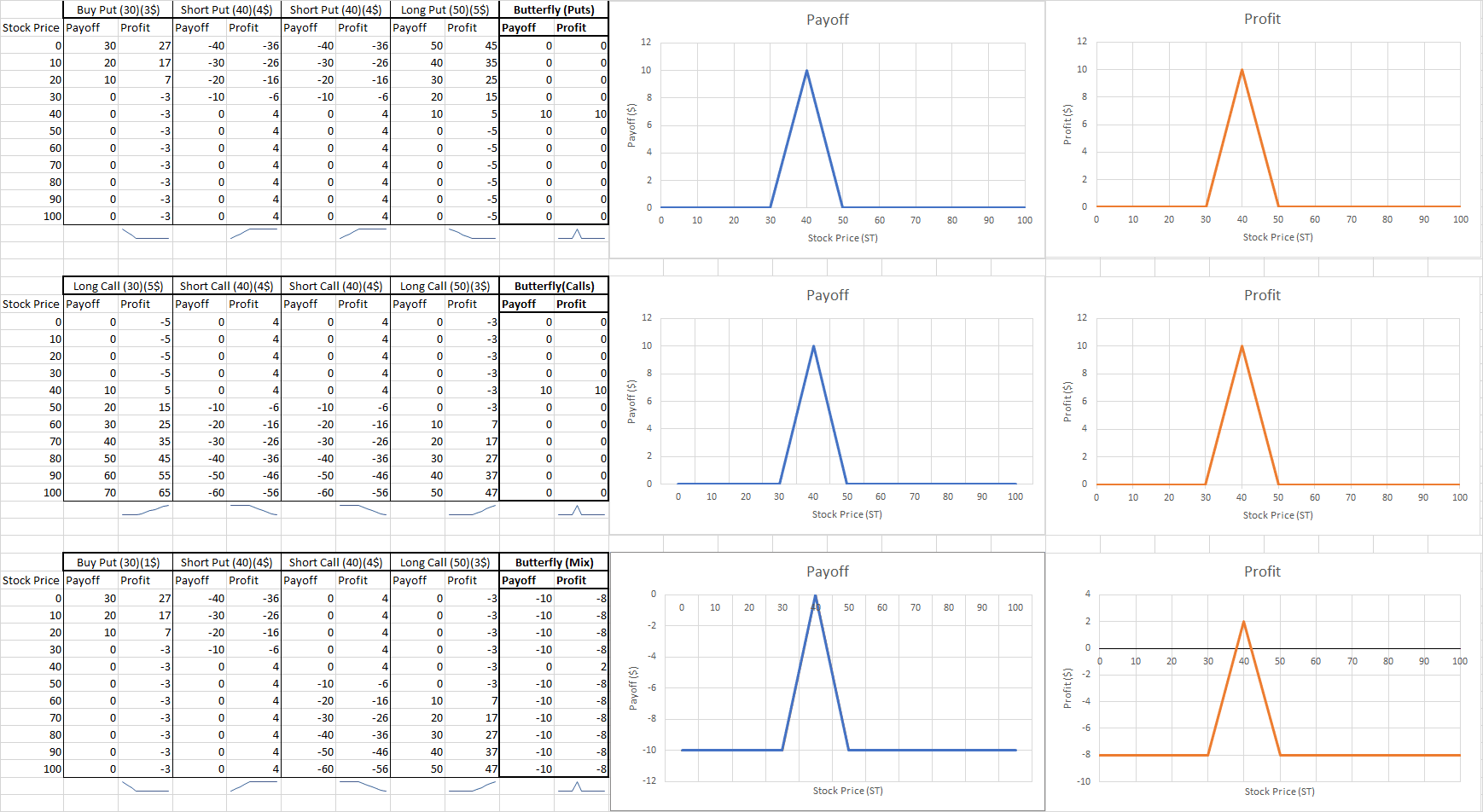
A butterfly is a volatility bet that the trader can implement to protect against large fluctuations, or to gain on volatility.
A Strangle is a volatility bet where you simultaneously long a put at Strike Price 2 and long a put at Strike Price 1, betting the stock price will make a big movement in either direction. This is similar to a Straddle, but the trader shorts the stocks instead of buying them (but the profit is basically the same)
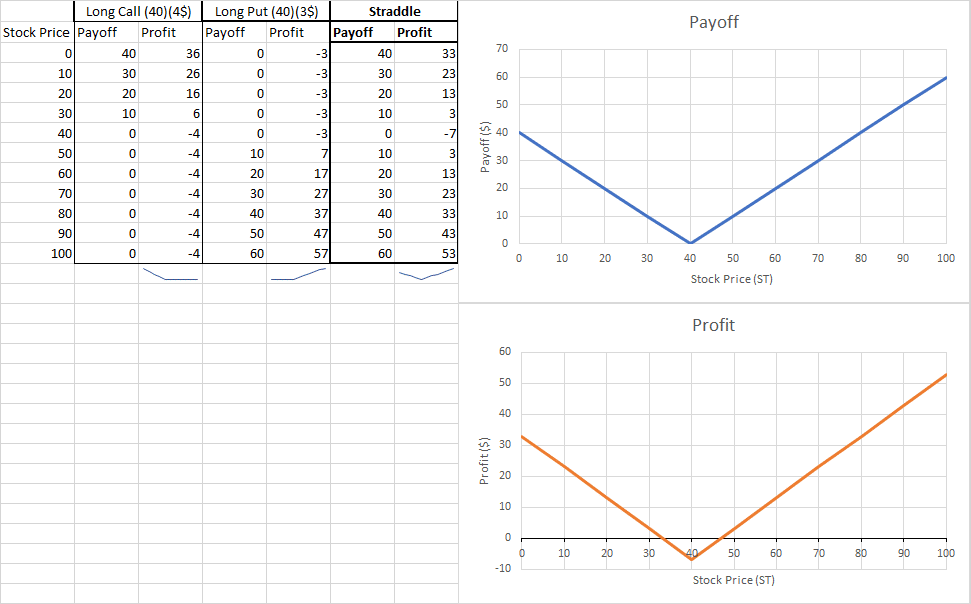
Straddles an option strategy that profits with volatility. You simultaneously buy long a call at Strike Price 1 and long a put at Strike Price 1. This creates a triangular shaped payoff and profit graph where the reward is based on the volatility of the stock – you’ll make a profit if the stock’s price makes a BIG move in either direction, but take a loss if it doesn’t move much.
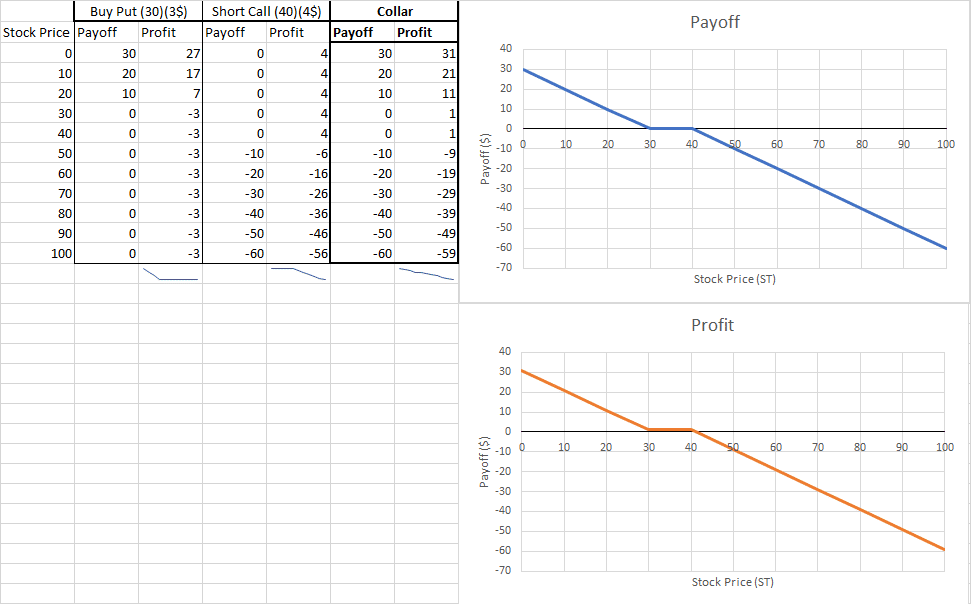
A bullish collar is a protection strategy where you simultaneously buy a call at strike price 1 and sell a put at strike price 2. This strategy is for investors who has a bullish perception on the underlying asset. We can also create a “bearish” collar by simultaneously buying a put at strike price 1 and selling a call at strike price 2.
A ratio strategy is an option strategy that is created by having X amount of call options at Strike Price 1 and shorting Y amount of call options at Strike Price 2. This strategy is used when the investor thinks the price won’t move much, but they want to get a bigger profit based on a slight movement up or down.
A box spread is an option strategy that is created by combining the components of the bull spread and the bear spread. In theory, a box spread should always have a zero profit and zero loss, but some investors use them if they see that current options prices aren’t fully “priced in”. In many cases, the commissions charged for the trades needed for this spread will be greater than the profit.
A bear spread is a strategy where you simultaneously buy a call option at Strike Price 1 (some amount higher than the current market rate), and sell a call option at Strike Price 2 (some amount lower than the current market right). This is used if the trader thinks the price of the stock will go down, but not by much. It limits both the risk and reward.
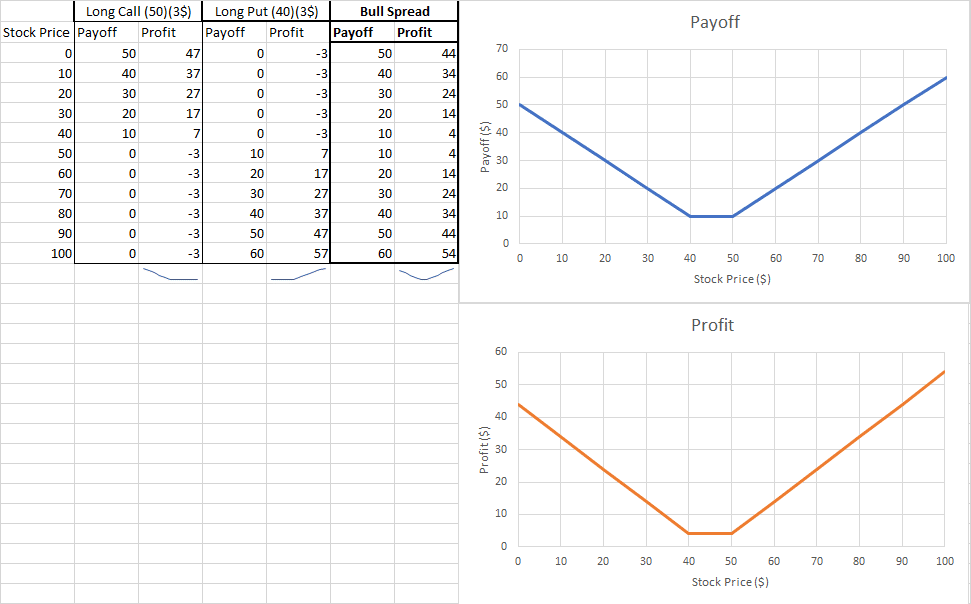
A bull spread is a strategy where you simultaneously buy a long call at Strike Price 1, and sell a call for Strike Price 2 (some higher amount). Use this strategy if you think that a stock’s price will go up above your Point 1, but not as high as your Point 2.
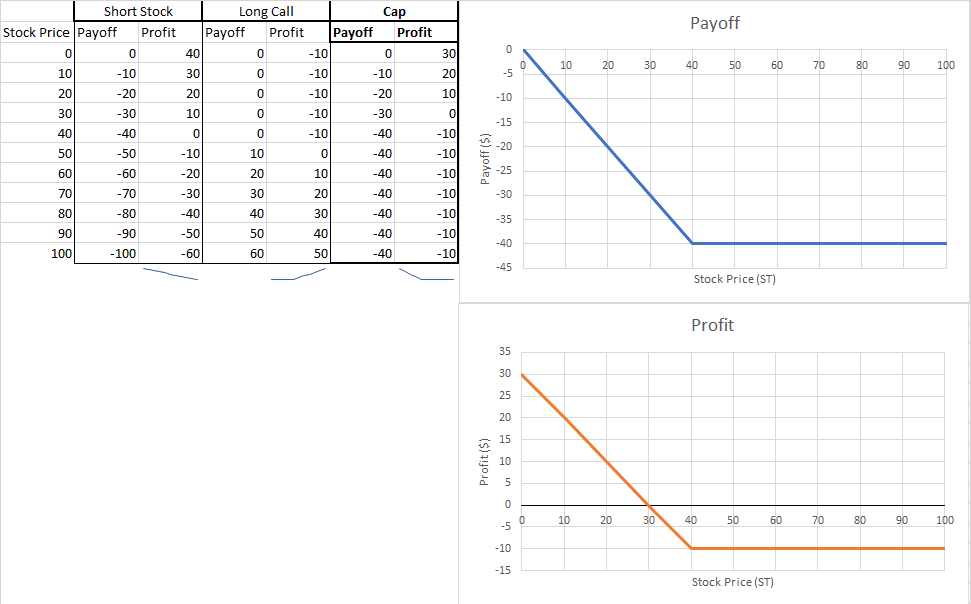
A cap is an options protection strategy where you simultaneously have a short position on a stock and a long call for the same underlying asset. Adding a long call to your open position means that you have the right to cover your short at the strike price.
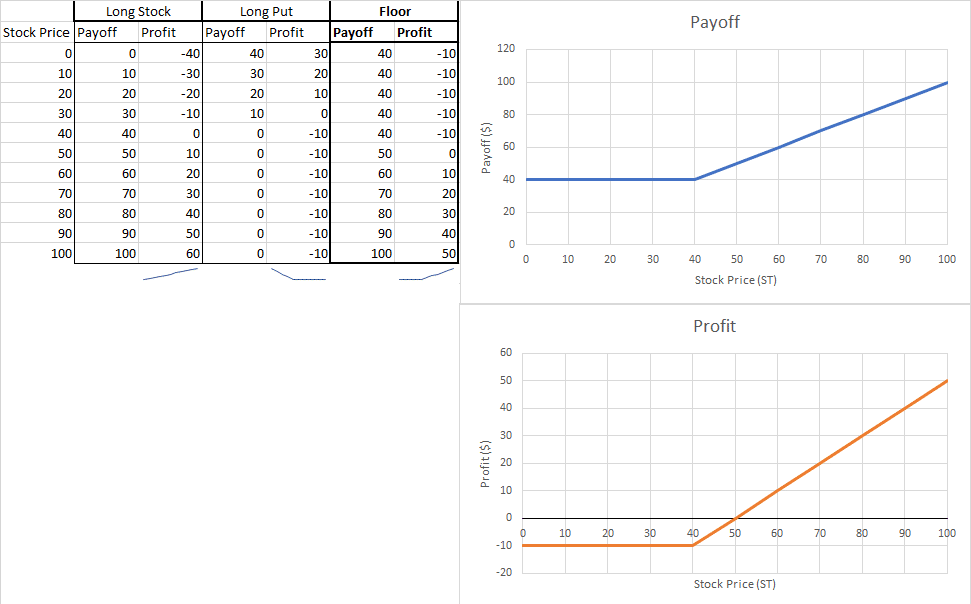
A floor is an options insurance strategy where you simultaneously have a long open position on a stock and a long put for the same underlying asset. Adding a long put to your open position means that if the stock’s price starts to fall, you still have the right to sell it off at the price specified by your option.
A covered put is an options insurance strategy where you simultaneously have a short open position on a stock and sell a put option for the same underlying option. This means you’re shorting a stock, but give someone else the right to sell you that stock at certain price in the future. You would use this if you were certain a stock’s price wasn’t going to go up, but you weren’t sure if would go down either – so you make a bit more money if the price doesn’t change.
A covered call is an options insurance strategy where you simultaneously own a stock and sell a call option for the same symbol (usually for a higher price than what you paid for it). This gives someone else the right (but not obligation) to buy your stock from you later at a specific price. If the underlying stock’s price goes up, the buyer will exercise the option and buy the shares. If the price goes down, the seller of the option keeps both the stocks and the price of the options.
A long call is a term used when you own a call option for an underlying asset. A call option is a contract where the buyer has the right (not the obligation) to exercise a buy transaction at a specific strike price at or before an expiration date. In the world of trading, owing a long call means that you have a contract that gives you the right to buy the underlying asset at a specific price, before a maturity date.
A short call is a term used when you sell a call option for an underlying asset. If you use this type of option, you’re selling someone else the right to buy a stock from you at a certain price in the future. If the stock’s price goes down, you keep the money you made by selling the option. If the stock’s price goes up, you are required to sell the stock at the agreed upon price, taking a loss.
A long put is a term used when you own a put option for an underlying asset. A put option is a contract where the buyer of the put has the right (not the obligation) to exercise a sell transaction at a specific strike price before an expiration date. In the world of trading, owning a long put means that you have a contract that gives you the right to sell the underlying asset at a specific price, before a maturity date.
A “short put” is selling a put option on an underlying asset. Short Puts are used by an investor who thinks a stock’s price is not going to go down. For example, with this type of trade, you would sell a Put option to someone else – giving them the right to sell a stock to you at the price you agreed on. If the price of that stock goes above that price, you keep the price of the option. If the price goes down, you’ll be required to buy the underlying stock at the Put price.
See the full listing of available corporate and treasury bonds available on our platform!
Spots are very easy to trade (if your contest allows it). Simply choose the action like you would with a stock, select the quantity and the spot you wish to trade from the dropdown from the Spots trading page. Click on this post for more details.
Click on this article to get answers to common questions about trading bonds.
If allowed in your contest, you can trade options using the specific options trading page described in the article. Click on this post for three options trading tips.
Trading Future Options acts like trading a normal option, but replacing the underlying stock with an underlying future. Read this post for a few future options trading tips!
Future Options are exactly what their name implies – an option on a futures contract.
Read this article for three crucial futures trading tips!
Includes industries, currencies, metals, interest rates/bonds, grains/oil seeds, food/fibers, and livestocks!
Calendar includes grains, metals, currencies, energies, financials, meats, softs and indices.
Option strategies allow you select any number of pros and cons depending on your strategy, that cannot be done with simply owning or shorting the stock. Read this article for more details on option strategies!
A straddle is an investment strategy that involves the purchase or sale of an option allowing the investor to profit regardless of the direction of movement of the underlying asset, usually a stock. There are two straddle strategies, a long straddle and a short straddle. Click on this post to learn more about the differences between these two straddle strategies.
This article can help you decipher options symbols into meaningful information to help you understand the option at hand!
When trading mutual funds on this system, there are a few differences to keep in mind compared to trading stocks. Click on this post for three mutual fund trading tips!
Options Spreads are option trading strategies which make use of combinations of buying and selling call and put options of the same or varying strike prices and expiration dates to achieve specific objectives (hedging, arbitrage, etc.).
If you’ve started buying a few stocks, you will probably be interested in diversifying your portfolio between various sectors. Click on this post to find out how our Quotes Tool can help you diversify your portfolio.
Your transaction history page will show you all the orders you’ve placed that have gone through. Click on this post to learn about its features and uses.
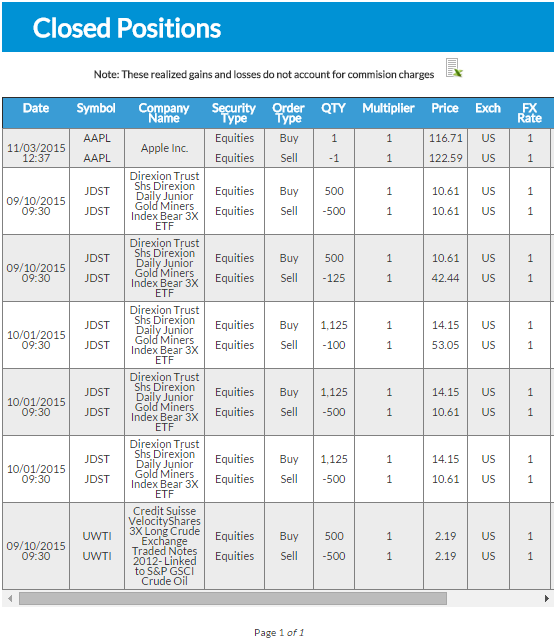
Your closed positions page will show an estimated profit and loss from all positions you’ve “Closed” (bought then later sold, or shorted and later covered. Click on this article to read about its features.
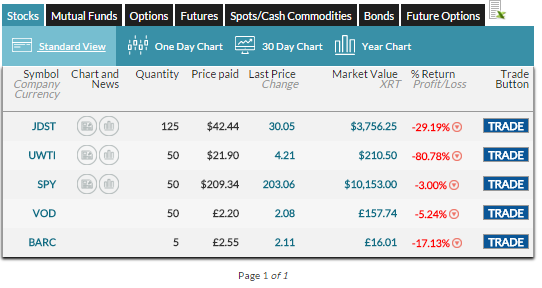
This post will help you locate your Open Positions page!
Spot and Futures contracts are a standardized, transferable legal agreement to make or take delivery of a specified amount of a certain commodity, currency, or an asset at the current date. The price is determined when the agreement is made.
Futures Contracts are a standardized, transferable legal agreement to make or take delivery of a specified amount of a certain commodity, currency, or an asset at the end of specified time frame.
Our Quotes Page provides a variety research tools both for beginners and for those looking to do more advanced research. Click on this article to learn about the various tools found on the quotes page, and what they can offer.
An option allows you to pay a certain amount of money (the option price) to allow you to buy or sell a stock at the price (strike price) you decided on when buying the option.
Option holders have the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell the underlying instrument at a specified price(strike price) on or before a specified date(exercise date) in the future. Exercising the option is using that right to to buy or sell the underlying instrument.
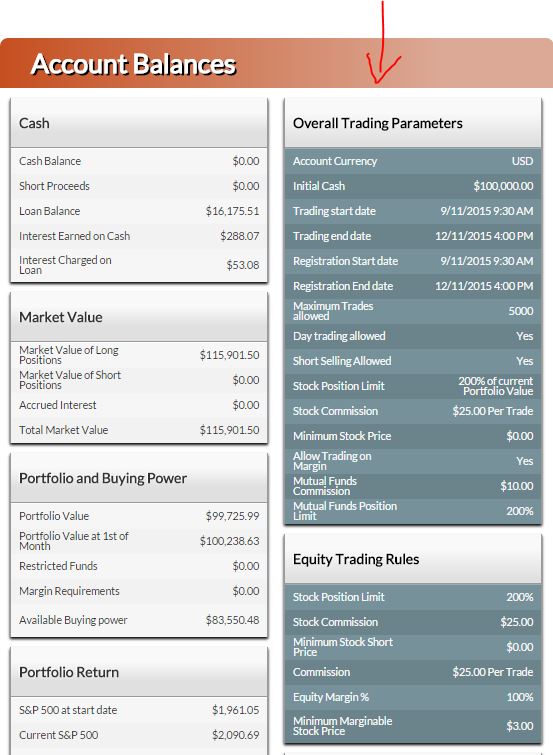
Calculating your buying power can be tricky, and it gets trickier with more complex contest rules. This will be a quick primer on how to see exactly how your buying power is calculated, what affects it, and how to recover it when you want to make more purchases.
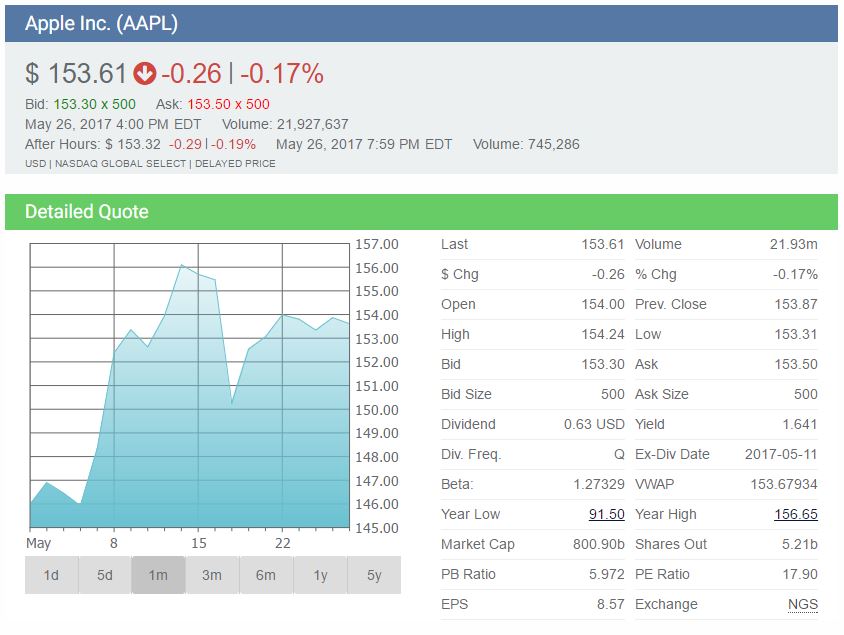
A stock quote represents the last price at which a seller and a buyer of a stock agreed on a price to make the trade. Stock quotes also contain information about the volume, high and low prices of the day and year, and more.
Stocks are a share of ownership of a company. If you own a stock, you are involved in some of its management decisions, and you are entitled to some of the company’s profits.
Mutual Funds come in several different “flavors”, but the core concept is always the same: the fund is a pool of money contributed from many different investors that are used to purchase a bundle of securities. They are professionally managed, so you are basically buying a piece of a larger portfolio.
“ETF” stands for “Exchange Traded Fund”, which is exactly how it sounds; they are like mutual funds in many ways, but they trade on a normal stock exchange like a stock, with their value being determined both by the value of the underlying assets and the value of the ETF itself.
Bonds are essentially a much more formal I.O.U (I owe you) used to borrow money. You buy the bond in return to interest over a given period of time.
ETFs are collections of assets into bundles you can invest in all at once, the most popular ones follow indecies (such as SPY following the S&P 500), which is one way for an investor to build a diverse portfolio without holding dozens of individual positions. However, using financial derivatives and debt, there are also “Leveraged ETFs”, which amplify the risks, and returns, of whichever index it is following. Read this article for a list of Leveraged ETFs.
Market Orders, Limit Orders, Stop Market Orders, Stop Limit Orders and Trailing Stop Orders! Each one is used differently to balance a trading strategy – usually so you can place your orders and wait for prices to match your conditions